5 Steps to Choosing the Right Heat Shrink Tubing
Heat shrink tubing can be obtained in a multitude of materials, sizes, and configurations and can be the right solution for many use-situations including:
- Electrical Insulation of bare wires or wire joints
- Bundling for loose wires
- Identification of wires and wire bundles
- Aesthetics for branding and other purposes
- Abrasion protection
- Strain relief
To navigate the nearly infinite variety of heat shrink tubing in the market here are 5 steps to determine the right type of heat shrink for your application.

Step 1: Industrial, Military/Aerospace vs. Medical Application
While the vast majority of heat shrink tubing can be used in industrial applications (provided all other application requirements are satisfied), when it comes to military/aerospace applications or medical applications additional considerations have to be accounted for.
Military/Aerospace heat shrink applications will commonly require a product that conforms to specific MIL-specs such as the very common SAE-MIL-DTL-23053/5 “General Specification for Electrical, Heat Shrinkable, Insulation Sleeving”. These specifications can govern the various aspects of the product including but not limited to continuous operating temperature ratings, colors and color designators, dimensions and tolerances, and many physical properties deemed appropriate by the standard. Due to their proven rigor and wide acceptance, many industrial applications will also reference MIL-specs for ease of design and procurement. For Industrial applications, some applications require UL or CSA which is not always available for every configuration of heat shrink tubing (for example clear-colored Polyolefin heat shrink is not available in UL or CSA).

Heat shrink tubing for medical applications is widely used in surgical devices, general medical instruments, and balloon/stent applications. Medical-grade heat shrink can vary drastically from Industrial-grade products in their materials of construction and general design characteristics, as well as how they are manufactured and controlled for quality, consistency, and traceability.
Please reference Heat Shrink Tubing: Medical Grade vs Industrial Grade for additional information
Step 2: Single Wall vs. Dual Wall (Adhesive-lined)
Single-wall tubing (also known as General Purpose tubing) is the most common type of heat shrink and is suitable for most insulation, sealing, and strain relief applications. It provides the flexibility and “form fit” shrinkability that is desired in these applications.
Dual-wall heat shrink has an internal adhesive lining that when heated with a heat shrink gun, will melt, flow, and bond around the encapsulated parts and provide an excellent layer of moisture-protection that is desired in more severe applications.
Please reference Single Wall Tubing vs. Dual Wall Tubing for additional details.
Step 3: Materials of Construction
The type of material used for heat shrink tubing is the primary determinant of its performance properties, from maximum temperature rating to chemical and electrical properties. PVC and Polyolefin heat shrink are the two most common materials of construction:
- Polyolefin heat shrink: provides a higher temperature rating than PVC while providing excellent chemical and electrical properties, as well as superior flexibility.
- PVC heat shrink: very cost-effective and available in a broad array of colors including custom colors.
Please reference Heat Shrink Tubing Materials Comparison Chart for additional materials details and products.
Step 4: Correct Sizing (Diameters and Shrink Ratios)
Typically heat shrink tubing will be denoted by a nominal size, such as 3/32 inches, which corresponds to the expanded inner diameter prior to recovery (Expanded ID). The heat shrink tubing in question will also have a maximum recovered inner diameter (Max Recovered ID) which is the largest inner diameter the tubing will have after it has been heated and shrunk. The most common shrink ratios of before and after diameters are 2:1 and 3:1 but others are available depending upon application and construction.
A good best practice is to not specify a recovered ID that is too constrictive compared with the encapsulated wires or connectors, which can in turn lead to splitting and failure of the heat shrink to retain its structural integrity. Lastly, all heat shrink should be tested in a pre-production trial to gauge the quality and repeatability of the selection and application process.
Please reference What is Heat Shrink Ratio and How Do I Determine Which Tubing I Need? for additional sizing guidelines and information.
Step 5: Additional Considerations
Once the application, wall-construction, material of construction and sizing are analyzed and selected there are a few optional but still important factors to take into consideration:
Cut-to-Length vs. Continuous Spool: Most heat shrink tubing is available in continuous spools that can be cut to the appropriate length during the manufacturing process. While this results in increased flexibility it does require the additional measuring and cutting steps that can interrupt a production process. Alternatively, customized pre-cut heat shrink tubing is available which provides exact length(s), tolerances, and quantities in a production-ready state. Some common types of tubing are available as off-the-shelf, pre-cut lengths, and packages.
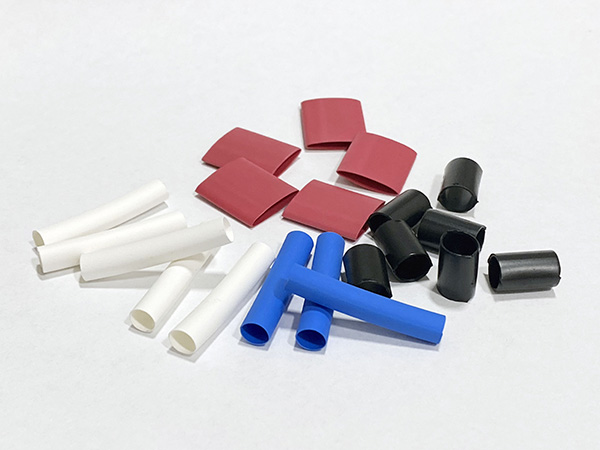
Heat shrink tube colors: Some applications require specific colors due to aesthetics or identification purposes. The most common Polyolefin and PVC heat shrink are typically available in multiple standardized colors though single wall, general purpose heat shrink can oftentimes be available in more numerous color options than dual wall, adhesive lined heat shrink. Some heat shrink materials, such as Kynar, Polyolefin, and PVC (amongst others), are available in clear, see-thru materials while several materials can be had with customized color matching per application requirements.
Marked heat shrinking tubing: heat shrink can also be marked or printed on for identification purposes. This can include bar codes, logos, or any number of information types.

Conclusion
Going through these steps and considering the application, single vs dual wall, material, size, and color should help you narrow down what heat shrink tubing is right for your situation. While LAPP Tannehill offers a variety of resources to understand heat shrink tubing, our customer service team is also available to answer any questions. Contact us via chat, contact form, or call us at 800.633.6339.
5 Steps to Choosing the Right Heat Shrink Tubing
Heat shrink tubing can be obtained in a multitude of materials, sizes, and configurations and can be the right solution for many use-situations including:
- Electrical insulation of bare wire or wire joints
- Bundling for loose wires
- Identification of wires and wire bundles
- Aesthetics for branding and other purposes
- Abrasion protection
- Strain relief
To navigate the nearly infinite variety of heat shrink tubing in the market here are 5 steps to determine the right type of heat shrink for your application.


Step 1: Industrial, Military/Aerospace vs. Medical Application
While the vast majority of heat shrink tubing can be used in industrial applications (provided all other application requirements are satisfied), when it comes to military/aerospace applications or medical applications additional considerations have to be accounted for.
Military/Aerospace heat shrink applications will commonly require a product that conforms to specific MIL-specs such as the very common SAE-MIL-DTL-23053/5 “General Specification for Electrical, Heat Shrinkable, Insulation Sleeving”. These specifications can govern the various aspects of the product including but not limited to continuous operating temperature ratings, colors and color designators, dimensions and tolerances, and many physical properties deemed appropriate by the standard. Due to their proven rigor and wide acceptance, many industrial applications will also reference MIL-specs for ease of design and procurement. For Industrial applications, some applications require UL or CSA which is not always available for every configuration of heat shrink tubing (for example clear-colored Polyolefin heat shrink is not available in UL or CSA).


Heat shrink tubing for medical applications is widely used in surgical devices, general medical instruments, and balloon/stent applications. Medical-grade heat shrink can vary drastically from Industrial-grade products in their materials of construction and general design characteristics, as well as how they are manufactured and controlled for quality, consistency, and traceability.
Please reference Heat Shrink Tubing: Medical Grade vs Industrial Grade for additional information


Step 2: Single Wall vs. Dual Wall (Adhesive-lined)
Single-wall tubing (also known as General Purpose tubing) is the most common type of heat shrink and is suitable for most insulation, sealing, and strain relief applications. It provides the flexibility and “form fit” shrinkability that is desired in these applications.
Dual-wall heat shrink has an internal adhesive lining that when heated with a heat shrink gun, will melt, flow, and bond around the encapsulated parts and provide an excellent layer of moisture-protection that is desired in more severe applications.
Please reference Single Wall Tubing vs. Dual Wall Tubing for additional details.
Step 3: Materials of Construction
The type of material used for heat shrink tubing is the primary determinant of its performance properties, from maximum temperature rating to chemical and electrical properties. PVC and Polyolefin heat shrink are the two most common materials of construction:
- Polyolefin heat shrink: provides a higher temperature rating than PVC while providing excellent chemical and electrical properties, as well as superior flexibility.
- PVC heat shrink: very cost-effective and available in a broad array of colors including custom colors.
Please reference Heat Shrink Tubing Materials Comparison Chart for additional materials details and products.
Step 4: Correct Sizing (Diameters and Shrink Ratios)
Typically heat shrink tubing will be denoted by a nominal size, such as 3/32 inches, which corresponds to the expanded inner diameter prior to recovery (Expanded ID). The heat shrink tubing in question will also have a maximum recovered inner diameter (Max Recovered ID) which is the largest inner diameter the tubing will have after it has been heated and shrunk. The most common shrink ratios of before and after diameters are 2:1 and 3:1 but others are available depending upon application and construction.
A good best practice is to not specify a recovered ID that is too constrictive compared with the encapsulated wires or connectors, which can in turn lead to splitting and failure of the heat shrink to retain its structural integrity. Lastly, all heat shrink should be tested in a pre-production trial to gauge the quality and repeatability of the selection and application process.
Please reference What is Heat Shrink Ratio and How Do I Determine Which Tubing I Need? for additional sizing guidelines and information.
Step 5: Additional Considerations
Once the application, wall-construction, material of construction and sizing are analyzed and selected there are a few optional but still important factors to take into consideration:
Cut-to-Length vs. Continuous Spool
Most heat shrink tubing is available in continuous spools that can be cut to the appropriate length during the manufacturing process. While this results in increased flexibility it does require the additional measuring and cutting steps that can interrupt a production process. Alternatively, customized pre-cut heat shrink tubing is available which provides exact length(s), tolerances, and quantities in a production-ready state. Some common types of tubing are available as off-the-shelf, pre-cut lengths, and packages.
Heat Shrink Tube Colors
Some applications require specific colors due to aesthetics or identification purposes. The most common Polyolefin and PVC heat shrink are typically available in multiple standardized colors though single wall, general purpose heat shrink can oftentimes be available in more numerous color options than dual wall, adhesive lined heat shrink. Some heat shrink materials, such as Kynar, Polyolefin, and PVC (amongst others), are available in clear, see-thru materials while several materials can be had with customized color matching per application requirements.
Marked Heat Shrinking Tubing
Heat shrink can also be marked or printed on for identification purposes. This can include bar codes, logos, or any number of information types.


Conclusion
Going through these steps and considering the application, single vs dual wall, material, size, and color should help you narrow down what heat shrink tubing is right for your situation. While LAPP Tannehill offers a variety of resources to understand heat shrink tubing, our customer service team is also available to answer any questions. Contact us or call us at 800.633.6339.
